Chances are, earwax and its accumulation haven’t been subjects of extensive consideration for you, except perhaps during ear hygiene routines. Still, it’s crucial to have an understanding of its purpose and how it develops.
So why does earwax accumulate?
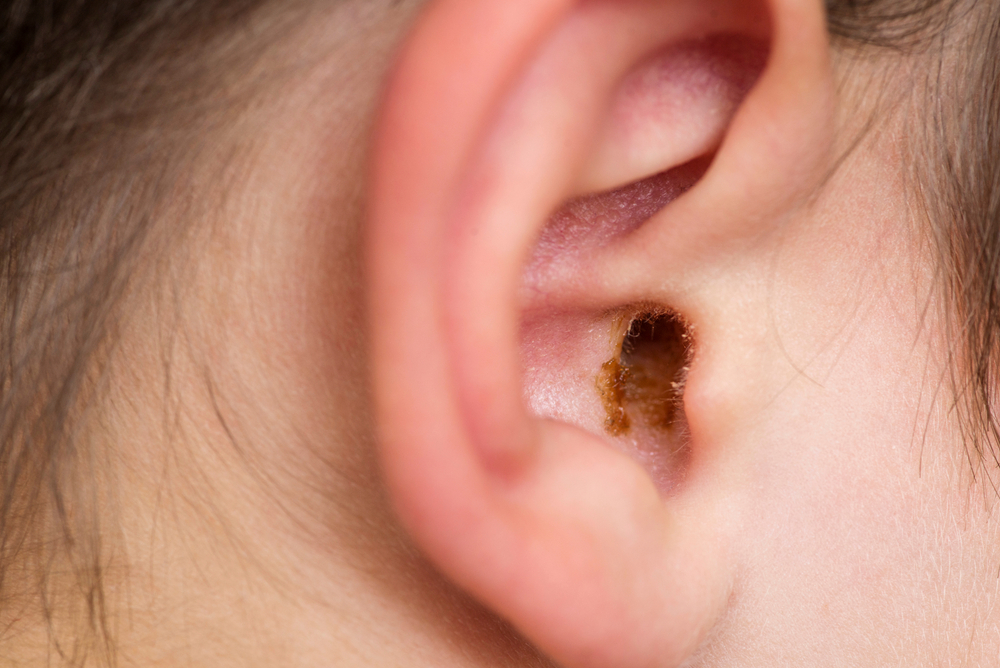
Earwax, scientifically called cerumen, is a thick combination of debris, hair, skin particles, sweat, and ceruminous gland secretions. Earwax will appear as a waxy substance that will normally be yellow, orange, brown, or even grey.
While the production amount of earwax varies from person to person, adults usually produce less earwax than kids. Moreover, adult earwax tends to be darker and harder compared to that of children.
Earwax gets discharged or washed out after going by the outer ear canal and reaching the opening of the ear.
Why do we need earwax?
Here are a few crucial functions that earwax serves:
- Before things such as dust, dirt, or other external debris go further up into the ear canal, earwax acts as a barrier.
- Fending off potential infections that might develop within the ear canal.
- Protecting and lubricating the skin lining the ear canal, thereby preventing dryness and itchiness.
Earwax obstructions
Impacted earwax is a prevalent problem, but it’s typically the only time you need to be concerned about it. Impacted earwax can stem from narrow or unusually shaped ear canals impeding the natural movement of earwax toward the ear’s opening.
Wax can be accidentally crammed up into the ear canal by utilizing poor cleaning methods like using cotton swabs.
Individuals grappling with hearing loss who make use of earplugs or hearing aids are also susceptible to experiencing ear canal blockages.
How is hearing affected by too much earwax?
The occurrence of earwax blockages may yield mild discomfort and dampen auditory health.
Also, substantial accumulations of earwax can induce tinnitus, a sensation of ringing in the ears.
Neglected earwax obstructions might escalate into middle ear infections, perforated eardrums, or enduring hearing loss as a result of acoustic trauma.
Dealing with impacted earwax
Should you think you have an earwax blockage, consulting us promptly is imperative. Depending on the extent of the obstruction, you might be advised to make use of over-the-counter wax softening drops or a bulb syringe for delicate irrigation to relieve the condition.
If you’re worried about your earwax buildup, call us right away to schedule an appointment.
